CONCEPT OF CHILD HEALTH
The term ‘pediatrics’ is derived from the Greek words, ‘Pedia’ means child, ‘iatrike’ means treatment and ‘ics’ means branch of science. Thus, pediatrics means the science of child care and scientific treatment of childhood diseases. Pediatrics is synonymous with child health.
Pediatrics can be defined as the branch of medical science that deals with the care of children from conception to adolescence in health and illness. It is concerned with preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children.
Children are major consumers of health care. In India, about 35 percent of total population are children below 15 years of age. They are not only large in number but also vulnerable to various health problems and considered as special risk group. Majority of the childhood sickness and death are preventable by simple low-cost measures. Disease patterns and management of childhood illness are different than that of adult. Children always need special care to survive and thrive. Good health of these precious members of the society should be ensured as prime importance in all countries. As said by Karl Meninger “What is done to children, they will do to the society.” Children are the wealth of tomorrow.
A child is unique individual, he or she is not a miniature adult, not a little man or woman. The childhood period is vital because of socialization process by the transmission of attitude, customs, and behavior through the influence of the family and community. Family's cultural and religious belief, educational level and ways of living influence the promotion and maintenance of child health. Children are vulnerable to disease, death and disability owing to their age, sex, place of living, socioeconomic status and a host of other variables. They need appropriate care for survival and healthy development.
The triad problems, poverty, population explosion and environmental stress are great threat towards child health in developing countries. Better nutrition, education (especially of girls) and family planning are essential aspects to improve child health. Healthy well nourished children develop better mentally and benefit more from education. Better education associated with more health knowledge, better health practices and more use of health services.
Factors Affecting Child Health
The important factors affecting the health of children are mainly maternal health, family health, socioeconomic situation, environment, social support and available health care facilities.
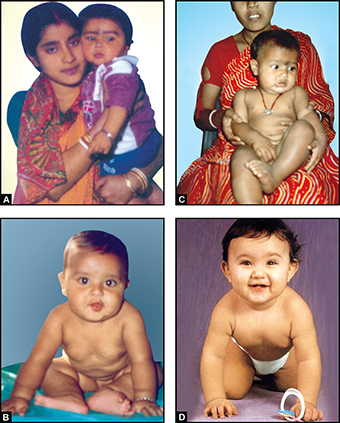
Maternal health is a major determinant of child health. The healthy mother brings forth a healthy baby with better chance of survival (Figs 1.1A to D).2
Figs 1.1A to D: Healthy mother and healthy children: (A) Healthy mother and child of a rich family; (B) Healthy infant of 6 months age; (C) Healthy mother and healthy child of a poor family; (D) Healthy infant of 9 months age
Child health is adversely affected, if the mother is malnourished or diseased. Mother's age, parity, prepregnant health, antenatal care and lack of spacing between two children affect the health of the child.
Child health is greatly depending upon family health. It depends upon family's physical and social environment which includes the lifestyle, culture, customs, taboos, rituals, religious practices, traditional habits, child bearing and child rearing practices, like son-complex, neglect to female child, etc. Family size, family relationship and family stability also influence the child health. For example, number of episodes of childhood diarrhea increases with the size of the family and prevalence of malnutrition increases with more than four children in a family. So, fewer children would mean better nutrition, better health care, less morbidity and lower infant mortality.3
The socioeconomic condition of the family is a very important factor in child health. The physical and intellectual development of children varies with the socioeconomic status of the family. Parent's education, profession, income, housing, urban or rural living, industrial life, etc, are significant factors which influence on child health. Poverty, ignorance, superstition, illiteracy especially mother's illiteracy and sickness pass from one generation to the next. The differences in health status between rich and poor can be observed in all age groups but particularly striking among children.
Environment plays a very great role as determinants of infant and childhood morbidity and mortality. Insanitary and hostile environment are responsible for various illnesses like infections, infestations, accidents, etc. Home and family hygiene, local epidemiological conditions, insufficient supply of safe water, inadequate disposal of human excreta and other waste, an abundance of insects and other disease carriers are the continuous threat to child health. Healthy environmental stimulation as interpersonal relationship is an essential factor for child's development. Congenial family relationship, healthy interaction with neighbors, teachers, schoolmates and playmates, exposure to mass media like radio, television, magazines are significant requirements for psychological and intellectual development of children.
Social support measures from the community and organized health care systems are indispensable for improvement and maintenance of health status of children (Figs 1.2A to F).
TRENDS IN CHILD HEALTH CARE
Historically, the concept of pediatrics was limited to the curative aspects of diseases peculiar to the children. Hippocrates (460-370 BC) made many significant observations on disease found in children and devoted a great part of his treatize to children. Galen of Rome (1200–1300 AD) wrote on the care of infants and children. Rhazes of Arab (850–923 AD) devoted much of his treatize to the subject of childhood illness. The first printed book on Pediatrics was in Italian (1472) by Bagallarder's “Little Book on disease in Children”. The first English book on children's disease was “Book of Children” written by Thomas Phaer (1545 AD).
The world's first Pediatricians were two Indians, Kashyapa and Jeevaka, of sixth century BC. Their pioneering works on child care and childhood disease are as relevant today as many of the modern concepts of child health. Sushruta, also wrote many aspects of child rearing and Charka wrote about care and management of newborn.
Child health care has changed dramatically in recent years due to advances in medical knowledge and understanding of emotional response of children. Advancement of understanding of different aspect of human development influences the changing concept of health. Health exists when an individual meets minimum physical, physiological, intellectual, psychological and social aspects to function appropriately for their age and sex level. Illness is the situations when individual experiences a disturbance in any of these areas that prevents functioning at appropriate level. Thus, attention is directed to psychosocial as well as physiological characteristics of health and illness.
Modern concept of child health emphasizes on continuous care of ‘Whole child’. According to UNICEF, assistance for meeting the needs of children should no longer be restricted to only one aspect like nutrition, but it should be broad based and geared to their long-term personal development ensuring holistic health care of children.
At present, in child health care more emphasis given on preventive approach rather than curative care only. Primary health care concept with team approach and multidisciplinary collaboration are adopted for child care. The challenge of this time is to study child health in relation to community, to social values and social policy. Increased public awareness, consumerism and family participation in child care are newer trends. Family health, a new concept is accepted for the care of children in their families and families in society. Need based, problem oriented, risk approach care is practiced for better child health.
In developed countries child health care extended up to adolescent, whereas in developing countries and in India, child care is extended up to 10 to 12 years of age. Recently special emphasis is given on adolescent health through RCH package services in our country. Special attention is given on the children at-risk like, orphans, destitute, disastrous, pavement dwellers, slum dwellers, child labors and handicapped children. Movement against gender bias, female fetocide, child abuse and neglect and maltreatment are in highlight at present.
Interest of the political leaders and understanding the importance of child health, constitution of national health policy for children and implementation of various health programs for improvement of child health are great achievements for children. Population control and family welfare approach, improvement of educational status specially women education and women empowerment, involvement of government and nongovernment organizations, political commitment and special budgetary allocation for child health activities, international guidance by WHO, UNICEF and other child welfare organizations for improvement of child health are promising aspects towards survival, health and well-being of children.
Growth of subspecialities for the superspecialized care of children is recent trend. The subareas are neonatology, perinatology, pediatric surgery, pediatric cardiology, pediatric neurology, pediatric hematology, pediatric nephrology, preventive pediatrics, child psychology, child psychiatry, pediatric intensive care unit, neonatal intensive care unit, etc.4
Figs 1.2A to F: Children in need for support services: (A) Teenage mother (second gravida); (B) Young mother with four daughters waiting to have a son; (C) Smiling lady in presence of several problems; (D) Malnourished children of urban slum; (E) Malnourished child of 2 years; (F) Children in need
5Medical science is advancing in every moment. So child health will also progress by various movements towards the aims to improve the survival and well-being of all children, as per WHO theme of the year 2005, “Healthy mothers and healthy children.”
CHILD HEALTH PROBLEMS
In the developing country like India, the child health care givers are facing a large numbers of problems. The major health problems include low birth weight, malnutrition, infections and infestations, accidents and poisoning, behavioral problems, etc. (Figs 1.3A to E).
- Low birth weight (LBW): It is the single most important determinant of the chances of survival, and healthy development of children. In countries, where the incidence of LBW infants is less, their preterm birth is the major cause. But where the proportion is high (e.g. in India), the majority of cases are related to fetal growth retardation, i.e. IUGR (Intrauterine growth retardation). WHO estimated that globally about 17 percent of all live births are LBW babies. In India, it is about 26 percent of all live births, in which more than half of these are born at term. Government of India wished to control this problem and decrease the incidence to 10 percent by the year 2000 but not achieved till now.
- 6Malnutrition: It is the most widespread condition affecting health of children. Inavailability and scarcity of suitable food, lack of money for purchasing food, traditional beliefs and taboos about child's diet and insufficient balanced diet are resulting in malnutrition. It is the underlying and associated cause of childhood illness and death among the under-five age group. It makes the child susceptible to infection, slower recovery from illness and higher mortality. Malnutrition in infancy and childhood leads to growth retardation. Undernourished children do not grow to their full potential of physical and mental abilities. The most frequent nutritional deficiency states are protein-energy malnutrition, vitamin— ‘A’ deficiency, nutritional anemia, iodine deficiency, etc.
- Infections and parasitic infestations: These are very common in children. The leading childhood infections are diarrhea, respiratory infections, measles, tuberculosis, pertussis, poliomyelitis, neonatal tetanus and diphtheria. HIV/AIDS is the emerging life-threatening infection and children are innocent victims of this condition. Beside these infections, systemic infections like meningitis, encephalitis, hepatitis, typhoid fever, urinary tract infections are also commonly found in children. Malaria and intestinal parasitosis including round worm, hookworm, tapeworm, giardiasis and amebiasis are frequently seen in children due to poor environmental sanitation, inadequate hygienic measures, unhygienic food and unsafe water.
- Accidents and poisoning: These are relatively more important child health problems in developed countries. But in developing countries like India, accidents are frequent among children especially the home accidents like burns, fall and poisoning due to inefficient child rearing practice. Outdoor accidents are also increasing in numbers among children specially road traffic accidents.
- Behavioral disorders: These are another increasing child health problems due to disturbances in family relationship, inadequate parent-child interaction, broken family, lack of education, inappropriate socioeconomic support and situational unrest. Juvenile delinquencies, educational backwardness, habit disorders, personality problems, emotional disturbances, sexual promiscuity and psychosomatic illnesses are frequently observed in children nowadays. The importance of special care for behavioral problems is recognized in most countries.
The presence of large numbers of problems in child health summon for acceptance of priority-based risk approach care. It is applicable in child health to minimize the childhood morbidity and mortality by appropriate management in time with special intensive care. The basic criteria for identifying ‘at risk’ infants and children include the followings:
- Birth weight less than 2.5 kg
- Twin births
- Birth order 5 or more
- Spacing of children less than 2 years
- No breastfeeding or insufficient breastfeeding along with artificial feeding
- Failure to gain weight during three successive months
- Weight below 70 percent of the reference standard
- History of death of two or more siblings before the age of 24 months
- Death of either or both parents
- Children with PEM and severe acute infections like diarrhea, measles, pertussis, etc.
DISEASE PATTERNS IN CHILDREN
There are some variations of disease pattern in children from country-to-country. But in India and its neighboring countries, a remarkable similar pattern is observed regarding frequency of diseases responsible for hospitalizations of infants and children.
It is observed in our health institutions that up to one-third of total pediatric admissions are due to diarrheal diseases and up to 17 percent of all deaths in indoor pediatric patients are diarrhea related. Diarrheal diseases are major public health problem among children under the age of 5 years.
Acute respiratory infections (ARI) are another major cause of death. Hospital records show that up to 13 percent of inpatient deaths in pediatric wards are due to ARI. The proportion of death due to ARI in the community is much higher as many children die at home. About 14 percent hospital admission are due to ARI.
Another important cause of pediatric admissions in hospitals is vaccine preventable diseases, that is approxi-mately 15.5 percent. Death due to vaccine preventable diseases is as high as about 25 percent.
Neonatal and perinatal conditions are responsible for about 4.6 percent of hospital admission and approximately 13 percent of all deaths. Other various conditions are responsible for one-third of total hospital admission in children and also for childhood death.
The common medical conditions found in the pediatric units are mainly meningitis, encephalitis, typhoid fever, hepatitis, nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, malaria, tuberculosis, kala-azar, thalassemia, etc. Gross malnutrition and serious systemic infections are found in combination in majority of the cases.
The common surgical conditions requiring hospital admissions in children are mainly related to congenital malformations. Other conditions are intestinal obstructions, acute abdomen, road traffic accidents, burns, fractures, etc.
STATISTICS RELATED TO CHILD HEALTH
Vital statistics are considered as indicators of health. Important vital statistics are birth rate and death rate. Child 7health status is assessed through measurement of mortality and morbidity. Morbidity data collected in specific survey can serve as indicators of comprehensive and specific health aspect. But morbidity data are scarce and poorly standardized. Measurement of growth and development is also an important indicator of child health status. Attention has been paid, recently, for systemic collection, interpretation and dissemination of data on growth and development.
In many countries, mortality rates are still the only sources of information about child health. The frequently used mortality indicators of child health care are perinatal, neonatal, postneonatal, infant and under 5 mortality rates.
Perinatal Mortality Rate
World Health Organization (WHO) expert committee on prevention of perinatal mortality and morbidity recommended a precise formula of perinatal mortality rate, i.e. “Late fetal and early neonatal deaths weighing over 1000 gm at birth expressed as a ratio per 1000 live births weighing over 1000 gm at birth.” It is calculated as:
Perinatal mortality rate has assumed greater significance as a yardstick of obstetrics and pediatrics care before and around the time of birth. It gives a good indication of the extent of pregnancy wastage as well as quality and quantity of health care available to the mothers and children.
Perinatal mortality is a problem of serious dimensions in all countries. It now accounts for about 90 percent of all fetal and infant mortality in the developed countries. In India, the perinatal mortality rate was reported about 32 per 1000 total live births with about 35 for rural and 22 for the urban areas (2010) as per SRS estimates. The national goal was to achieve a perinatal mortality rate between 30 and 35 by the year 2000 AD.
A number of social and biological factors are known to be associated with perinatal mortality. The risk factors are low socioeconomic status, high or low maternal age, high parity, short stature mother, bad obstetrical history, maternal malnutrition and severe anemia, multiple pregnancy, etc.
The causes of perinatal mortality are mainly antenatal, intranatal or postnatal asphyxia, LBW babies, congenital anomalies, birth injury and perinatal infections.
Reduction and prevention of perinatal mortality can only be possible with better maternal and child health services.
Neonatal Mortality Rate
Neonatal deaths are deaths occurring during the neonatal period, i.e. from birth to 28 completed days of life. It is calculated as:
Neonatal mortality is most difficult part of infant mortality to change. In India, it was about 33 per 1000 live births (2010). About 70 percent of all infant deaths occur within neonatal period and approximately 80 percent of neonates die during the first week of birth and first 24 hours is the greatest risk time.
Neonatal mortality is greater in boys throughout the world due to more fragility of boys than girls. The common causes of neonatal mortality include LBW, perinatal asphyxia, birth injury, difficult labor, congenital anomalies, hemolytic diseases of newborn, conditions of placenta and cord, diarrheal diseases, ARI and tetanus. Neonatal deaths can be reduced by adequate antenatal and intranatal care including essential neonatal care at all levels by preventing and managing the causes.
Postneonatal Mortality Rate
Postneonatal mortality rate is defined as the ratio of the postneonatal death in a given year to the total number of live births in the same year, usually expressed as a rate per 1000. It is calculated as:
Postneonatal mortality is dominated by exogenous factors, i.e. environmental and social factors. The main causes of death during postneonatal period are diarrhea and ARI. Malnutrition is the additional factor, which predisposes various infections. In developed countries, it is mainly caused by congenital anomalies. Postneonatal deaths increase with birth order and the girl children die more frequently than boys due to neglected care to the female children in terms of nutrition and health care.
In India, postneonatal mortality rate is estimated to be 20 in rural areas, 16 in urban areas and 19 per 1000 live births combined in rural and urban areas (2007).
Infant Mortality Rate
Infant mortality rate (IMR) is defined as “the ratio of infant deaths registered in a given year to the total number of live births registered in the same year, usually expressed as a rate per 1000 live births”. It is calculated by the formula:
8Infant mortality rate is universally regarded as a most important sensitive indicator of the health status of community. It is considered as an indicator of level of living of people and effectiveness of MCH services.
There are wide variations between countries or regions in the level of infant mortality. The world average of IMR for 2004 has been estimated at about 54 per 1000 live births. The worst rates were in Afghanistan (121.63) and the lowest IMR of less than 3 per 1000 live births in Japan, Sweden Hongkong, Singapore and Monaco.
India is still among high IMR countries, though it has come down to 44 per 1000 live births in 2011. There is statewise variation with highest in MP—59, and UP and Orissa—57 and Kerala as low as 12 per 1000 live births. National target is set to bring down the IMR to less than 28 per 1000 live births within the year 2015.
The principal causes of IMR in India are LBW, ARI, diarrheal diseases, congenital malformations, and infections, especially umbilical sepsis. There are several factors which interact to cause infant mortality. Biological and socio-economical factors influence more on the infant death. There is no single specific health program or a single set of action that can reduce IMR. As the etiology of IMR is multifactorial, so it requires multipronged approaches. Certain important measures to reduce IMR include lowest birth rate, highest literacy rate, specially female literacy and improvement of primary health care. Other preventive measures include prenatal nutrition, prevention of infections including six-killer diseases, exclusive breastfeeding, growth monitoring, family planning, environmental sanitation, simple hygienic measures and socioeconomic development.
Under-Five Mortality Rate (Child Mortality Rate)
United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF) defines the under-5 mortality rate as the “annual number of deaths of children aged under 5 years, expressed as a rate per 1000 live births”. The rate is computed by the formula:
Child mortality rate measures the probability of dying in between birth and exactly 5 years of age. The UNICEF considered this rate as the best single indicator of social development and well-being rather than GNP per capita. It reflects nutritional status, income, health care and level of basic education of the population.
The global average for under-5 mortality rate in 2008 was 65 per 1000 live births. In developed countries the rate was 7 per 1000 live births and in least developed countries, it was 158 per 1000 live births in 2002.
In India, child mortality rate in 2010 was 59 per 1000 live births. It is about 34 percent of all deaths. It was 242 per 1000 live births in 1960 and has declined significantly during the past years due to decline in infant mortality. This reduction is largely related to drop in deaths due to vaccine preventable diseases as well as drop in deaths from ARI and diarrhea.
The major causes of child mortality among children under 5 years in developing countries are acute respiratory infections, neonatal and perinatal threats, diarrhea, malaria, pertussis, neonatal tetanus, tuberculosis, measles, malnutrion, accidents and HIV related diseases.
The basic measure of infant and child survival is the reduction of under-five mortality. The difference in the survival rates of children in developed and developing countries is a grim pointer to the third world's need for preventive services. The child survival can be best achieved by breastfeeding, adequate nutrition, clean water supply, immunization coverage, oral rehydration therapy and birth spacing.
On the occasion of World Health Day, 2005, WHO reported that one child in twelve does not reach his/her fifth birthday. Each year 10.6 million children under the age of five years die from a handful of preventable and treatable conditions. Nearly all these deaths occur in low and middle income countries. WHO, celebrated World Health Day on 7th April, 2005, with the theme “Healthy mothers and healthy children“ and the slogan “Make every mother and child count”, to make the health of women and children a higher priority and to improve survival, health and well-being of these precious group.
Selected Statistics Related to Child Health in India
A. Distribution of population below 15 years of age | 32.1 percent of total population (2007) | |
B. Crude birth rate | – 22.1 per 1000 midyear population (2010) | |
C. Crude death rate | – 7.2 per 1000 midyear population (2010) | |
D. Mortality indicators: | ||
a. Infant mortality rate | – 44 per 1000 live births (2011) | |
b. Under-5 mortality rate | – 59 per 1000 live births (2010) | |
c. Neonatal mortality rate | – 33 per 1000 live births (2010) | |
d. Postneonatal mortality rate | ||
e. Early neonatal mortality rate | – 25 per 1000 live births (2010) | |
E. Prevalence of LBW babies | – 28 percent of all live births (2003–2008) | |
F. Services coverage: | ||
a. Infants fully immunized | – 43.5% | (2008) |
i. BCG vaccination | – 87% | (do) |
ii. DPT and OPV vaccination | – 66% | (do) |
iii. Measles vaccination | – 70% | (do) |
b. Pregnant women-Tetanus toxoid | – 83.4% | (do) |
c. Antenatal care | – 75% | (do) |
d. Institutional delivery | – 47% | (2007–2008) |
G. Total fertility rate | – 2.6 | (2009) |
H. Urban and rural population ratio | – 31.16: 68.84 | (2011) |
I. Literacy rates | – 74.04% | (2011) |
CHILD HEALTH CARE IN INDIA
Children are the most important age group in all societies. Health status and health behavior of later life are laid down at this stage. Child health care should include specific biological and psychological needs that must be met to ensure the survival and healthy development of the child, the future adult.
Childhood period can be customarily divided for purpose of effective care into the different age-groups, i.e. infancy, preschool, school age, and adolescence.
Children under the age of 5 years are grouped with the mothers considering as vulnerable and risk group comprising about 32 percent of total population in India.
The mother and child health (MCH) services is the method of delivering health care to these special groups. The MCH services contain the preventive, promotive, curative and social aspects of obstetrics, pediatrics, family welfare, nutrition, child development and health education. The ultimate objective of MCH services is life-long health. The specific objectives for the services include reduction of morbidity and mortality rates for mother and children and promotion of reproductive health along with child health. Promotion of physical and psychological development of the child within the family can be possible by family participation in the comprehensive care of children through the MCH services.
The components of MCH services include six subareas, i.e. maternal health, family planning, child health, school health, care of handicapped children and care of children in special setting such as day care centers.
The MCH services, at present, are provided through reproductive and child health (RCH) program. The RCH program incorporates the components related to child survival and safe motherhood (CSSM), family planning and prevention of RTIs/STDs and AIDS. The services are provided in client-oriented, target-free, demand driven, high quality, participatory and decentralized approaches on the basis of needs of community.
Other than RCH program, various health programs are initiated by the Government of India to improve the survival of children. Nongovernment organizations and child welfare organizations also contributing towards better child health. Other child health services include integrated child development services (ICDS) scheme, under-5 clinics, school-health services, postpartum services through PP units, baby-friendly hospital initiative, child guidance clinic, etc.
Child health services are delivered through anganwadi centers (ICDS-center) at village level, subcenter clinics, PHC clinics, outreach services by home visit and camps and in hospital as indoors and outdoors. The child care is planned in various health institutions by the health workers in integrated and risk approach. Primary health care is now recognized as a way of making essential health care available to all, including children, by the multipurpose health workers, professional health workers, voluntary workers and field workers, like community health guides, traditional birth attendants, anganwadi workers, etc. The services are available both in urban and rural areas through different infrastructures. The specific low cost simple measures are organized for the child health care through various approaches for saving life of millions of children on priority basis.
RIGHTS OF THE CHILD
The united nations adopted the “Declaration of the Rights of the Child”, on 20th November, 1959, to meet the special needs of the child. India was a signatory to this declaration to give the child pride of place and to make the people aware of the rights and needs of children and duties towards them.
The ten basic rights of the child are:
- Right to develop in an atmosphere of affection and security and protection against all forms of neglect, cruelty, exploitation and traffic.
- Right to enjoy the benefits of social security, including nutrition, housing and medical care.
- Right to a name and nationality.
- Right to free education.
- Right to full opportunity for play and recreation.
- Right to special treatment, education and appropriate care, if handicapped.
- Right to be among the first to receive protection and relief in times of disaster.
- Right to be brought up in a spirit of understanding, tolerance, friendship among people, peace and universal brotherhood.
- Right to enjoy these rights, regardless of race, color, sex, religion, national or social origin.
A nongovernmental organization (NGO), Defence for Children International, Geneva; has been in operation since 1979, the International Year of the Child, to ensure ongoing, systemic international action, especially directed towards promoting and protecting the Right of the Child.
UNIVERSAL CHILDREN'S DAY
November, 14th is observed as universal children's day. It was started by the International Union for Child Welfare and the UNICEF. In 1954, the UN General Assembly passed a formal resolution establishing universal children's day and assigned to UNICEF the responsibility to promote the celebration of this annual day.
The World Summit for children (1990) agreed on a series of specific goals for improving the lives of children including measurable progress against malnutrition, preventable diseases and illiteracy. The vital vulnerable years of childhood should be given priority on society's concerns and capacities. A child has only one chance to develop normally and demands protection and commitment that never be superseded by any other priorities.
The realization that children have special needs and hence the special rights has given birth to an international law in the shape of convention on the ‘Rights of the child’. The provisions of the convention were confirmed in 1990 by the World Summit for Children.
The convention defines children as people below the age 18 years whose best interests must be taken into account in all situations. It protects children's right to survive and develop to their full potential with highest attainable standard of health care.
The social goals that have been accepted by almost all nations following the 1990 World Summit for Children were:
Overall Goals (1990–2000)
A one-third reduction in under-five death rates (or to 70 per 1000 live births, whichever is less):
- A halving of maternal mortality rates.
- A halving of severe and moderate malnutrition among the world's under-fives.
- Safe water and sanitation for all families.
- Basic education for all children and completion of primary education by at least 80 percent.
- A halving of adult illiteracy rate and achievement of equal educational opportunity for males and females.
- Acceptance in all countries of the convention on the rights of child including improved protection for children in especially difficult circumstances.
Protection for Girls and Women
- Family planning information and services to be made available to all couples to prevent unwanted pregnancies and birth which are ‘too many and too close’ and to women who are ‘too young or too old’.
- All women should have access to antenatal care, a trained attendant during child birth and referral facilities for high-risk pregnancies and obstetrical emergencies.
- Universal recognition of special health care and nutritional needs of females during early childhood, adolescence, pregnancy and lactation.
Nutrition
- A reduction in the incidence of low birth weight (below 2.5 kg) to less than 10 percent.
- A one-third reduction in iron deficiency anemia among women.
- Elimination of vitamin ‘A’ deficiency and iodine deficiency disorders.
- Information to all families about the importance of supporting women in exclusive breastfeeding for first four to six months of a child's life.
- Growth monitoring and promotion need to be institutionalized in all countries.
- Information to increase awareness about household food security in all families.
Child Health
- Eradication of poliomyelitis
- Elimination of neonatal tetanus and 90 percent reduction in measles cases and 95 percent reduction in measles deaths.
- Achievement and maintenance of at least 90 percent immunization coverage to infants and universal tetanus immunization for women in the child bearing years.
- A halving of child deaths caused by diarrheal diseases and 25 percent reduction if its incidence.
- A one-third reduction of child deaths caused by acute respiratory infections.
- Elimination of Guinea worm disease.
Education
NATIONAL POLICY FOR CHILDREN
The Government of India adopted a National Policy for children in August 1974, keeping in view the United Nations Declaration of the Rights of the child and the constitutional provisions.
The policy declares “it shall be the policy of the state to provide adequate services to children, both before and after birth and through the period of growth, to ensure their full physical, mental and social development. The state shall progressively increase the scope of such services so that, within a reasonable time, all children in the country enjoy optimum conditions for their balanced growth.”
According to the declaration, the development of children has been considered as integral part of national development. The policy recognizes children as the “nation's supremely important asset” and declares that the nation is responsible for their “nurture and solicitude”. It also emphasizes the priorities of children's program and special focus on child health, child nutrition and welfare of the handicapped and destitute children.
A number of programs were introduced by the Govt. of India, after the declaration of national policy for children. The important programs are ICDS scheme, programs of supplementary feeding, nutrition education, production of nutritious food, welfare of handicapped children, national children's fund, CSSM programs, etc.
The principles of India's National Policy for Children are as follows:
- A comprehensive health program for all children and provision of nutrition services for children.
- Provision of health care, nutrition and nutrition education for expectant and nursing mothers.
- Free and compulsory education up to the age of 14 years, informal education for preschoolers and efforts to reduce wastage and stagnation in schools.
- Out of school education for those not having access to formal education.
- Promotion of games, recreation and extracurricular activities in schools and community centers.
- Special programs for children from weaker sections.
- Facilities for education, training and rehabilitation for children in distress.
- Protection against neglect, cruelty and exploitation.
- Banning of employment in hazardous occupations and in heavy work for children.
- Special treatment, education, rehabilitation and care of physically handicapped, emotionally disturbed or mentally retarded children.
- Priority for the protection and relief of children in times of national distress and calamity.
- Special programs to encourage talented and gifted children, particularly from the weaker sections.
- The paramount consideration in all relevant laws is the “interests of children.”
- Strengthening family ties to enable children to grow within the family, neighborhood and community environment.
CHILDREN ACT
The children Act, 1960 (amended in 1977) in India, provides for the care maintenance, welfare, training, education and rehabilitation of the delinquent child. It covers the neglected, destitute, socially handicapped, uncontrollable, victimised and delinquent children. In Article 39(f), the constitution of India provides that “the state shall in particular direct its policy towards securing that childhood and youth are protected against moral and material abandonment.”
The Juvenile Justice Act, 1986, provides a comprehensive scheme for care, protection, treatment, development and rehabilitation of delinquent juveniles. The new Act has come into force from 2nd October 1987, after rectification of the inadequacies of the Children Act (1960). This Act was amended again in 2000 and 2006.
Juvenile Justice Act 2000
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2000, now amendment Act 2006 is an Act to consolidate and amend the law relating to juveniles in conflict with law and children in need of care and protection. The Act defines a juvenile/child as a person who has not completed the age of 18 years. It has two chapters—one for juveniles in conflict with law and other for children in need of care and protection. It also contains an exclusive chapter concerning rehabilitation and social reintegration of children. This Act promotes proper care, protection and treatment by catering to the developmental needs of children and by adopting a child friendly approach in the best interest of children and for their ultimate rehabilitation.
The needs of children and our duties towards them are enshrined in our constitution. The relevant articles are as follows:
- Article 24 prohibits employment of children below the age of 14 years in factories.
- Article 39 prevents abuse of children of tender age.
- Article 45 provides the free and compulsory education for all children until they complete the age of 14 years.
Other important Acts for child welfare are: “The Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, 1986”, “The Child 12Marriage Restraint Act 1978” “The Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956”, “Infant Milk Substitute, Feeding Bottles and Infant Foods (Regulation of Production, Supply and Distribution) Act 1992 and Prenatal Diagnostic Techinique (Regulation and Prevention of Misuse) act 1994.
Special attention has been given to the welfare of children in the five-year plans by the Government of India. Various schemes and programs have been introduced and implemented to achieve the goals of child health services.
Healthy children are future healthy citizens of the countries. So every attempts should be made towards better tomorrow for better survival of this precious group and to help them to grow into healthy adult. Promotion of child health should receive priority attention in all levels as new challenge of the 21st century. WHO, in 2005, emphasizes on healthy mothers and children. The aims and objectives of World Health Day, 2005, is to create momentum that compel national governments, international community, civil society and individuals to take action to ensure the health and wellbeing of mothers and children. These can be achieved by raising awareness, increasing understanding about the existing solutions and generating movement to stimulate collective responsibility and action to improve the survival, health and well-being of all mothers and children.